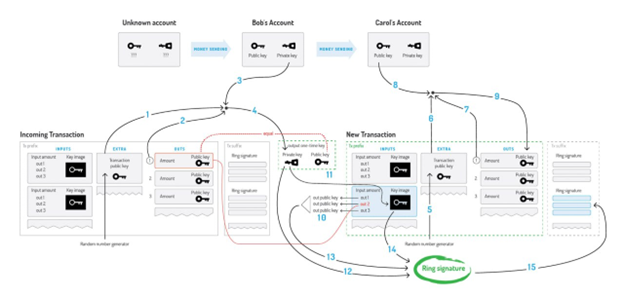
Biometrics have existed for many years, from a fingerprint on rice paper in China to sophisticated and expensive face recognition systems nowadays.
Throughout history, humans have sought ways to identify individuals for various aspects of life. As technology becomes more integrated into our daily lives and online transactions become more prevalent, authenticating identities has become essential. As scammers find new ways to deceive people, the integration of biometrics and the regulation by authorities to detect and prosecute illegal activities become paramount in our society.
Biometrics Overview
Biometrics involve securing a person’s biological information from unauthorized access. This practice has historical roots, but it gained formal scientific attention with the industrial revolution.
Historical Timeline
1892: Sir Francis Galton developed the first fingerprint classification system.
1903: New York state prisons began using fingerprints.
1960: Face recognition became semi-automated due to research by Woodrow W. Bledsoe.
1969: The FBI sought to automate fingerprint recognition.
1994: The Immigration and Naturalization Service developed IDENT for the U.S. Border Patrol, containing 1.8 million biometric identities by 1999.
Advancements in Technology
With the advancement of technologies such as Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML), the accuracy and security of biometric systems can be enhanced through adaptive algorithms that evolve to detect and fend off sophisticated cyber threats. Key areas where AI and ML are expected to impact biometric technology include:
- Improved accuracy and reliability
- Enhanced security measures
- Continuous authentication systems
Using these technologies, governments and enterprises can monitor and track user activities, which is crucial in industries such as banking and government.
Concerns and Challenges
There are concerns about the centralization and collection of biometric data, particularly regarding civil liberties and mass surveillance. These repositories of data are lucrative targets for malicious actors looking to exploit, manipulate, and profit from this data.
Market Potential
The future of biometric technology looks bright, not only for financial rewards but for societal benefits. Advantages of using biometrics include:
- Enhanced user experience
- Cost-effectiveness
- Better fraud prevention
- Increased efficiency
Comparison of Different Biometrics
The next table shows the different biometrics and features of each one of them.
Iris
Retina
Fingerprint
Hand Geometry
Writing & Signature
Voice
Face
Reliability
Very High
Very High
High
High
Medium
High
High
Ease of Use
Medium
Low
High
High
High
High
High
Prevention Against Attacks
Very High
Very High
High
High
Medium
Medium
Medium
Acceptance
Medium
Low
High
High
Very High
High
Very High
Stability
High
High
High
Medium
Low
Medium
Medium
Market Growth
It is estimated that the next generation of biometric technology in industries like law enforcement, tourism, immigration control, and data center protection is expected to grow to $94.2 billion USD by 2028.

Biometrics are used in various areas in the automotive industry, including access control for starting a vehicle using various biometric scanners, enable personalized vehicles for users to call up playlists, contacts, and preferred apps. The automotive industry alone is expected to grow at a rate of 22% from 2024 to 2030, generating $12 billion USD.

Key Industry Players
Top companies developing sophisticated biometric solutions include:
- HID Global Corp (US)
- Bio Key International (US)
- NEC (JPN)
- Thales Group (US)
Use Cases
Automotive Industry
State Farm, a US-based insurance firm, proposed a new auto insurance plan using biometric and automobile data to personalize rates. Their Emotion Management System (EMS) technology monitors various physiological parameters and provides stimuli to alter the driver’s behavior, enhancing safety.
Ford, on the other hand, is concentrating its efforts on developing technology that monitors driver’s health. Though still in its infancy, wearable technology has the potential to revolutionize the automotive industry in the next ten years.
Surveillance
Drones equipped with face recognition technologies can identify criminals and lost persons in crowds. Current technologies can recognize faces from certain distances and angles, and employing 3D models can improve recognition accuracy.
Airline industry
Delta Air Lines, in partnership with U.S. Customs and Border Protection, TSA, and Hartsfield-Jackson Atlanta International Airport, launched the first curb-to-gate biometric terminal in the U.S. at Atlanta’s Terminal F. This allows travelers to use face recognition technology throughout the check-in process and boarding.
Conclusion
Biometrics have long been used for identification purposes. With the rise in fraud and the growing need to protect identities, biometrics will play a crucial role in security. Companies are investing heavily in this technology due to its significant growth potential. As biometrics become more integrated into everyday processes, they will play an increasingly important role in our daily lives.
References